By Fred Ingham, head of international hedge fund investments, Neuberger Berman
 A quiet revolution is happening in hedge funds. Investors continue to allocate to the asset class, but the way they are allocating is changing, while its investor base is growing broader and becoming more inclusive.
A quiet revolution is happening in hedge funds. Investors continue to allocate to the asset class, but the way they are allocating is changing, while its investor base is growing broader and becoming more inclusive.
With both bond and equity markets facing major challenges, investors are increasingly seeking strategies that are not tied so tightly to the performance of the broader equity and fixed income markets. This trend has been picked up over several years by the Morningstar and Barron’s Alternative Investment Survey of U.S. Institutions and Financials Advisors, the 2014-15 edition of which was recently released.
Reporting the views of nearly 400 investors, it found 63% of advisors believe they will allocate more than one-tenth of client portfolios to alternatives over the next five years, compared with just 39% in the same survey for 2013.
Over several years the survey has showed continued growth in alternatives wrapped in more accessible registered fund structures that offer daily liquidity, as opposed to the more traditional, and exclusive, private funds. Assets in U.S. registered alternative funds have risen from less than $50 billion under management in 2008 to over $300 billion as of mid-2015. While growth has slowed from what Morningstar and Barron’s described as the “eye-popping” rates of 2013, money is still flooding into “multi-alternative” and managed futures retail products in particular, with many new funds having been launched to meet demand. The trend is spreading outside the U.S.: Strategic Insight’s SIMFUND database reveals a similar trajectory, showing the number of liquid alternative European UCITS and US 40-Act mutual fund products tripling to well over 1,500 since 2008.
Structures, not just strategies
Clearly, the latest developments in alternative investing are as much about investment structures as investment strategies. The survey report notes, for instance, strong positive flows into multi-alternative regulated funds coincide with dwindling traditional fund-of-hedge-fund assets.
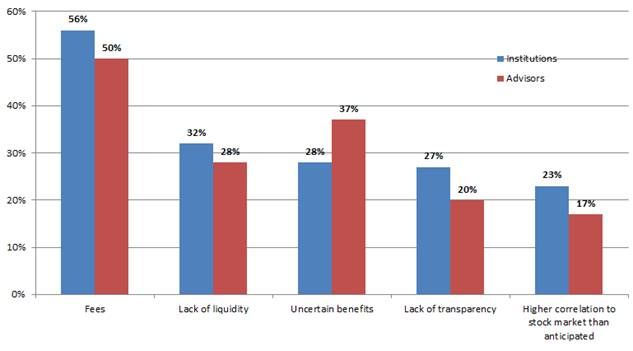
Indeed, while U.S. advisors, who tend to be heavier users of mutual funds for liquid hedge fund strategies, have been increasing their allocations, U.S. institutional investors more used to traditional hedge fund structures have been cutting back from the latter: the Morningstar and Barron’s survey found those expecting to allocate more than 25% to alternatives declined from 31% a year ago to 22% today. The survey report suggested they “may be tempering their enthusiasm as a result of fees, lockups and poor transparency in traditional hedge funds, as was the case with CalPERS’ announced decision to withdraw from hedge funds,” and these concerns came up when investors were asked what makes them hesitate before making alternatives allocations.
‘Top Reasons to Hesitate Investing in Alternatives’
(percentage of respondents)
Source: Morningstar and Barron’s, “2014–2015 Alternative Investment Survey of U.S. Institutions and Financial Advisors, July 2015.”
Investors moving their exposure to hedge fund strategies into the regulated fund world are addressing these following issues without throwing the baby out with the bathwater.
Fees:
The typical fee for a hedge fund used to be 2% asset-based management fee, with a 20% performance fee on top. Investing through a fund of funds at peak pricing could have added an additional 1% and 10%, respectively. Competition has brought costs down, but they remain high—and the addition of hurdle rates and high watermarks on performance fees adds complexity and variability.
While many UCITS still charge management and performance fees at higher, “hedge fund” levels, some providers are consciously bucking that trend and bringing fund expenses in line with typical U.S. practices. Although generally higher than those charged on most long-only mutual funds, management fees on alternative ’40 Act funds are generally set to compete with those on other specialist mutual funds, and are lower than fees charged by traditional hedge funds because they do not have performance fees, which are prohibited for funds offered to retail investors.
Redemption terms:
Many hedge funds allow only monthly or quarterly redemption and often include longer-term lockups after initial commitments. During the stressed markets of 2008, some hedge funds “gated” redemptions, only allowing a certain amount of cash to be withdrawn at any one time.
Mutual funds are required to offer daily redemption at a fund’s next NAV. (Again, while this is required for U.S. mutual funds, it is not always the case for regulated funds in other jurisdictions.) While some of the less liquid parts of credit markets may be out of bounds for funds offering daily redemptions, a multi-strategy, multi-manager liquid alternatives product offering daily redemptions at NAV should have access to a substantial portion of the hedge fund strategies available, minimizing selection bias.
Transparency:
Hedge funds often only report to investors once a month, with a delay, and position-level transparency is not the norm. Multi-manager alternative funds often utilize a separate account structure, as opposed to the traditional fund-of-funds model, and this ensures position-level transparency for the portfolio managers on a daily, or even real time, basis. This allows for greater risk oversight and improves the ability of the portfolio manager to react to changing market conditions. Additionally, certain regulatory requirements applicable to registered funds require that all securities be maintained at a custodian bank and, therefore, the fund maintains total control over its assets.
Corporate governance:
It is not always clear hedge fund directors are sufficiently engaged in governance, and in traditional funds of funds investors have little oversight of the selection of prime brokers, administrators and auditors. As part of the comprehensive regulation provided by ‘40 Act and UCITS, regulated funds’ boards, which include members independent of the manager, provide a much improved governance framework. For multi-manager funds, they can help improve the process of monitoring the underlying managers and often allow the fund, and not the underlying managers, to select and directly oversee other fund service providers.
An encouraging trend
The fact more and more products are being rolled out to fit this investor-friendly profile is encouraging. Morningstar and Barron’s have tracked 475 launches since 2009, and the 118 new products for 2014 represented a significant jump from the 89 that appeared in 2013.
This reflects an increasingly competitive hedge fund industry: managers are both more willing to adapt their hedge fund terms to match those of regulated funds and more willing to launch regulated funds to access a bigger pool of investors. This is happening largely without injurious hedge fund-style terms being smuggled into regulated fund structures, or the watering down of hedge fund strategies. That is why we believe this growing phenomenon has earned its distinguishing descriptor: “liquid alternatives.”
Also from Neuberger Berman: